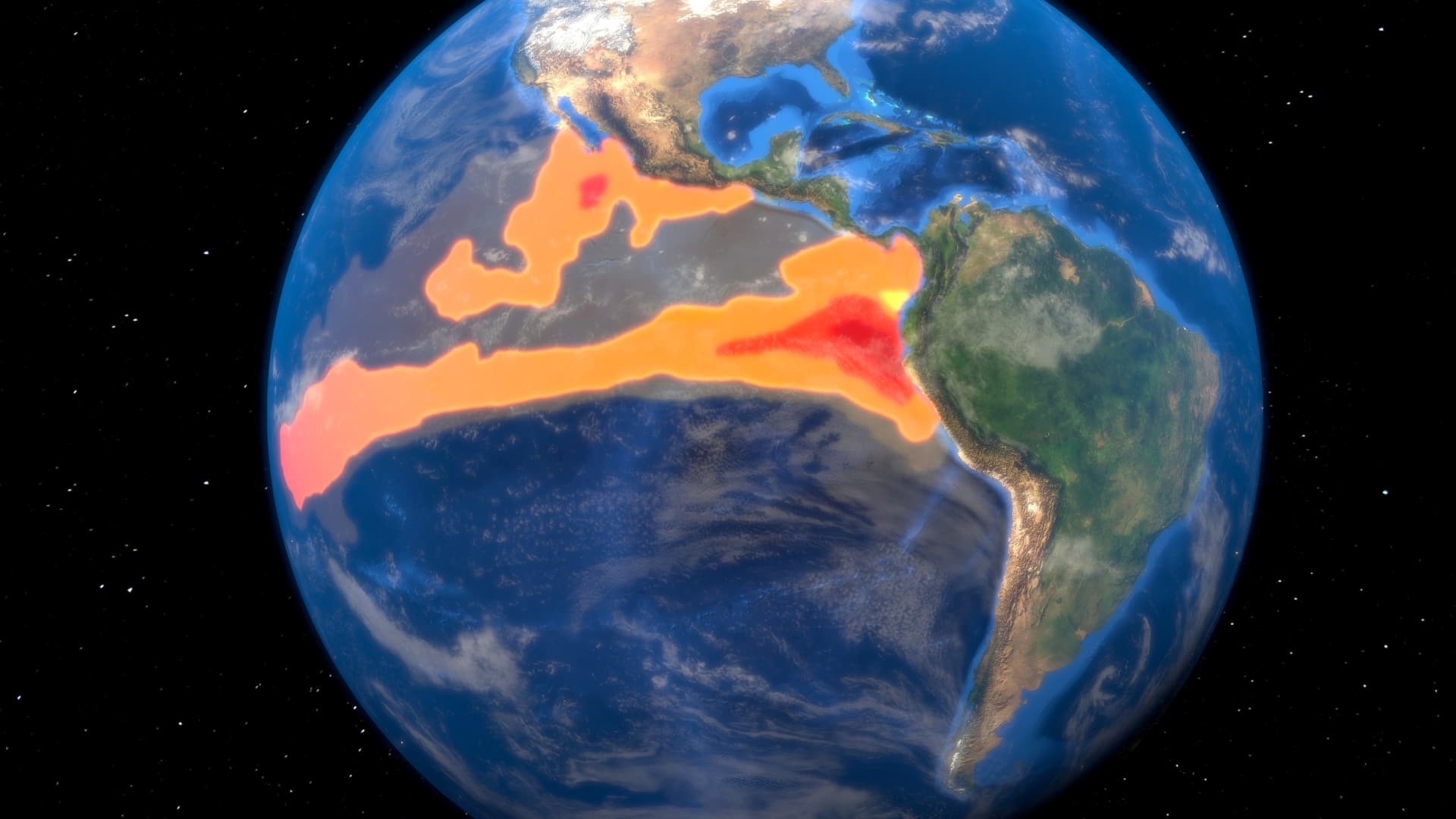
El Niño is the warm phase of the El Niño La Niña Southern Oscillation, or ENSO, that occurs across the tropical Pacific Ocean roughly every five years. The ENSO affects weather systems across the world, bringing extreme weather such as floods and droughts. El Niño generally causes drier conditions in Australia and Southeast Asia, and wetter and warmer conditions in the Americas.
Juan Gaertner/science Photo Library | Science Photo Library | Getty Images
A climate pattern called El Niño, which has the potential to bring warmer temperatures and more extreme weather conditions, has arrived and is expected to get stronger over the winter, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
“El Niño conditions are present and are expected to gradually strengthen into the Northern Hemisphere winter,” NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center said in an advisory published Thursday.
El Niño (“little boy” in Spanish) and La Niña (“little girl” in Spanish) are weather patterns in the Pacific Ocean that can impact weather conditions around the globe.
In the United States, a moderate to strong El Niño in the fall and winter correlates with wetter-than-average conditions from southern California to the Gulf Coast, and drier-than-average conditions in the Pacific Northwest and Ohio Valley, NOAA said. It also increases the chance of a warmer-than-average winter across the northern part of the U.S.
“We’ve been anticipating this for a few months and we are still waiting to see how big an event it will be,” Gavin A. Schmidt, the director of NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies, told CNBC. The first advisory watch for El Niño was issued on April 13, according to NOAA.
“El Niño tends to peak around December/January and it could be a minor event or a major one and the impacts that we’ll see will depend on that,” Schmidt told CNBC.
NOAA said there is an 84% chance of an El Niño with a greater than moderate strength and a 56% chance of a strong El Niño developing by the…
Read the full article here
Leave a Reply